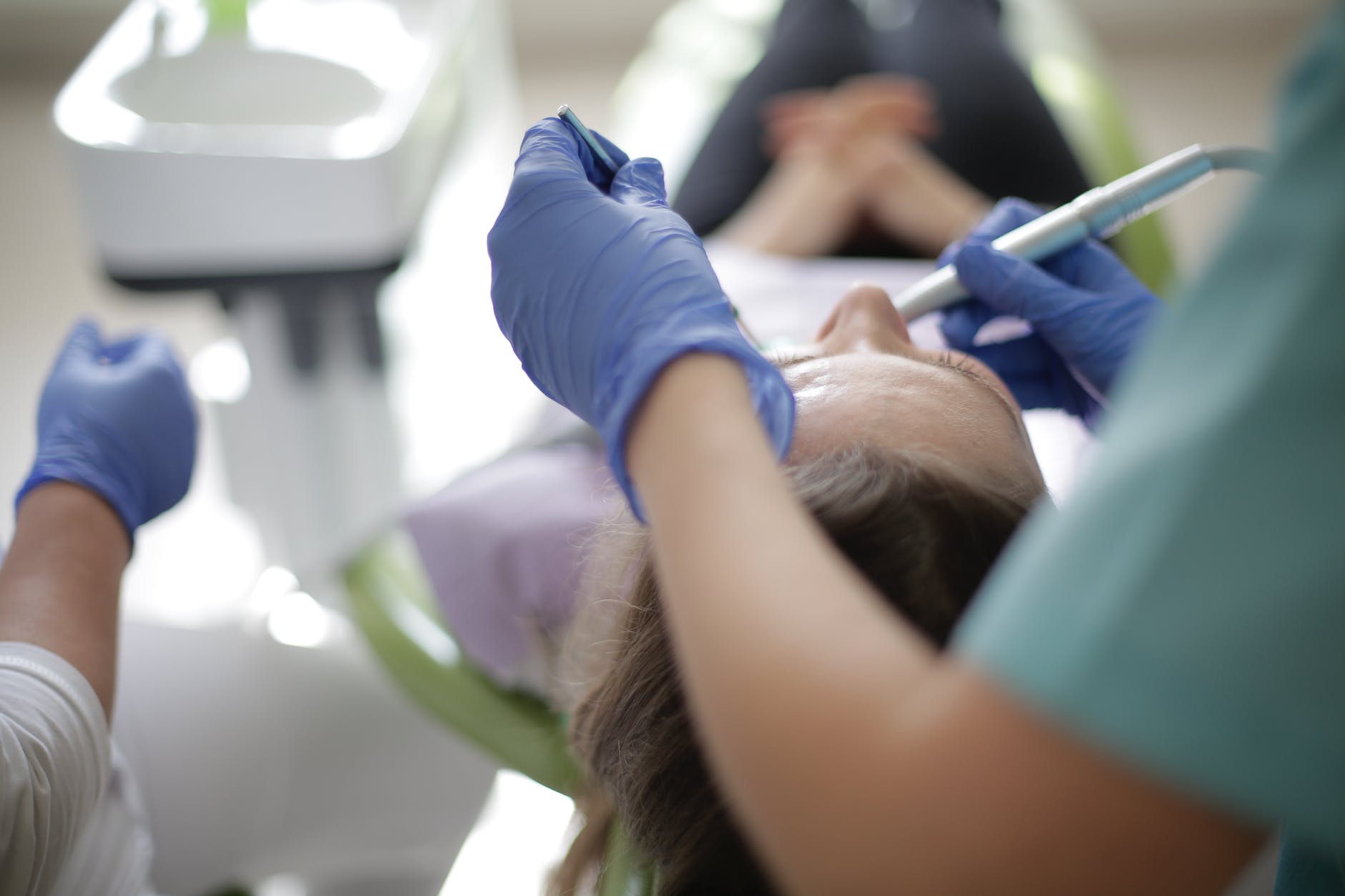
Periodontists are dental specialists who specialize in the mouth and teeth.
Dentists perform various critical duties for your teeth, gums, and more. On the other hand, a periodontist is a dentist who specializes in the gums and bones that support your teeth. To keep your teeth in good health, you need a periodontist Durham, a dentist specializing in gum and bone health.
A Periodontist is someone who specializes in the mouth and teeth.
Dentists at dental school can pursue a variety of career paths. In addition, dentists who want to become periodontists can pursue extra training.
What is the profession of a periodontist, and how does one become one? The American Academy of Periodontology defines a periodontist as “a dentist who specializes in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment [of] periodontal disease and the insertion of dental implants.”
Periodontists can also treat inflammation of the gums and teeth’s supporting bone. After dental school, periodontists go on to a residency program that can last three or more years. In addition, periodontists must finish residency programs and pursue further study in specific fields.
Periodontists: What Exactly Do They Do?
The goal of a periodontist is to maintain, repair, and restore as much bone and tissue as possible for the benefit of their patients. However, periodontists have approaches that fall into six categories of treatment for patients whose bone and tissue have reached the point of no return:
Procedures Using Hard Tissue
Bone grafting, bone reshaping, and tori excision are examples of osseous procedures, also known as invasive procedures.
Procedures involving the soft tissues
Glossoplasties and frenectomies are only a few treatments that perform on the mouth’s soft tissues.
Procedures for Extracting
When a patient’s tooth or teeth must remove, a periodontist will conduct an extraction. The removal of wisdom teeth is a common type of extraction. Another reason to have a tooth pulled is if the tooth is decayed.
Procedures for Dental Implants
The loss of a tooth due to trauma or periodontal disease is sometimes unavoidable. When a tooth is missing, an implant can be used to fill the gap. The titanium used in today’s dental implants is a delicate design, allowing your bone to integrate with it.
Procedures utilizing both soft and hard tissues in combination
Soft and complicated approaches are necessary for several processes. Periodontists commonly do pocket removal or gum surgery in conjunction with other procedures. An air pocket is formed between the gingival (gum) tissue and a tooth when the bone around a tooth recedes (where the tooth used to be). A periodontal probe is then use to measure the distance between the bone and the tooth. Without flossing, germs build up and produce an acid that destroys bones and other supporting components in their mouths. When this acid is present, your gums become inflamed, much like when you have a splinter in your finger. An excruciating Ack!
Millions of teeth have save because of this technique, and it has also helped alleviate discomfort and anguish for many more.
“Gummy” smiles, in which other gums appear to overwhelm a person’s smile, are another example of soft and hard tissue surgery. As it stands, a person’s gums extend too far below their teeth. So that a patient’s smile is as attractive as possible, periodontists perform gum recontouring surgery to expose more tooth structure.
Cosmetic surgery
Occasionally, a medical operation is unnecessary, but patients wish to improve their appearance. Cosmetic contouring inserted at this point. Cosmetic gum contouring is similar to gum surgery, and it’s popular among those who want an equal grin.